Most Important IAS topics (Subject-wise) for UPSC Prelims & Mains Exam
To prepare for the Union Public Service Commission, mainly four general studies paper exams have to be given, in these general studies paper, you have to read different subjects so that your general knowledge can be tested, through this 4 general studies Return papers are taken, through which the general knowledge of the students is checked, this nail is checked, we are telling you the important topic scores of all these general studies papers, from which you must read and understand so that you can get into the paper. To give better performance, we are telling you each subject wise and their important topics so that you will be able to improve your Union Public Service Commission preparation.
यूनियन पब्लिक सर्विस कमीशन की तैयारी करने के लिए प्रमुख रूप से चार जनरल स्टडीज पेपर की एग्जाम देने होते हैं इन जनरल स्टडीज पेपर में आपको अलग-अलग सब्जेक्ट को पढ़ना होता है ताकि आपके जनरल नॉलेज को टेस्ट किया जा सके इसी के द्वारा 4 जनरल स्टडीज रिटर्न पेपर लिए जाते हैं जिसके माध्यम से विद्यार्थियों के जनरल नॉलेज को चेक किया जाता है उनके इस कील को चेक किया जाता है हम आपको इन सभी जनरल स्टडीज पेपर के महत्वपूर्ण टॉपिक स्कोर बता रहे हैं जिससे आपको जरूर पढ़ना चाहिए समझना चाहिए ताकि आप पेपर में बेहतर परफॉर्मेंस दे सकें हम आपको प्रत्येक सब्जेक्ट वाइज तथा उनके महत्वपूर्ण टॉपिक को बता रहे हैं जिससे आप अपने यूनियन पब्लिक सर्विस कमीशन की तैयारी को बेहतर बना पाएंगे
GENERAL STUDIES 1
Indian Heritage & Culture
- How to Study Art & Culture?
- What is Art and Culture? What is the difference between the two?
- Architecture
- Sculpture
- Indian Paintings
- Religion
- Philosophy
- Indian Music
- Indian Dance
- Theatre
- Puppetry (कठपुतली)
- Indian Cinema and Circus
- Bhakti & Sufi Movement
- Language & Literature
- Fairs, Festivals and Craft: Fairs and festivals are an important part of any society in the world.
- Science & Technology[Art & Culture]
- Promotion and Preservation of Indian Heritage
- Pottery tradition in India: Evidence of pottery has been found in the early settlements of Mehargarh from the Indus Valley Civilization.
- Martial Arts in India: Martial arts mean “arts concerned with the waging of war”. Various Indian Martial arts have originated from various ancient war skills.
Ancient Indian History
- Prehistoric period
- Harappan / Indus Valley Civilization
- Vedic Age
- Mahajanapadas and Rise of Magadha
- Religious Reforms
- Iranian & Macedonian Invasion
- Mauryan Age
- Post Mauryan Age
- Gupta Age
- Sangam Age
- Regional Kingdoms
- Post Gupta Age
Medieval Indian History
After the death of Harshavardhana India witnessed significant changes, this period is also known as twilight of ancient India.
- Pataliputra permanently lost its prominence as symbol of sovereignty of India.
- Kanyakubja (kannauj) became symbol of sovereignty of India in early medieval times.
- For the control of kanyakubja (Ganga Yamuna doab region) three Indian dynasties waged continuous wars, which is known as triangular warfare. Palas , Prathiharas and Rashtrakutas participated in warfare.
- Decentralization was on its peak, paved ways for emergence of Indian feudalism.
- Many regional powers emerged powerful, political unity of India was shattered into pieces.
- A new ruling clan RAJPUTS
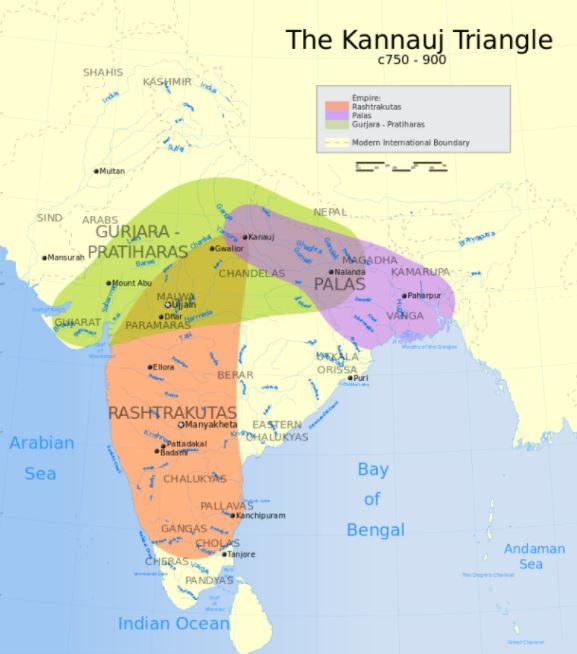
- Major Dynasties of Early Medieval Period
- Chola Empire
- Turkish conquest of India
- Rajput states
- Delhi Sultanate
- Mughal Empire (Including later Mughals)
- Maratha Confederacy
- Southern Dynasties
- Vijayanagara
- Bahamani Kingdom
- Religious Movements during Medieval Period
Modern Indian History
- Fall of Mughals
- Advent of Europeans
- India under East India Company’s Rule
- Administration
- Political policies
- British Expansion Policy
- Economic policies and their impact
- Foreign Policies
- Social Policies
- Indian Kingdoms in 18th Century
- Socio – Religious Reform Movements in the 19th and 20th CE India
- Changes in Indian Administration after 1858
- Growth of Political Ideas and Political Organizations (up to 1885)
- Foundation of the Indian National Congress
- National Movement (1885 – 1919)
- National Movement (1919 – 1939)
- Freedom to Partition (1939 – 1947)
World History
- Industrial Revolution
- French Revolution
- Nationalism in Europe
- Nation-State System
- Unification of Italy
- Unification of Germany
- Colonialism
- American Revolution
- World War I
- Russian Revolution
- Great Depression
- Fascism
- Nazism
- World War II
- Decolonisation
- Issues in Middle East
- Cold war
- Other Topics
- Arab Nationalism
- Israel-Palestine issue
- Integration of Europe
- Global Islamic terrorism
- Rise of China
World Geography
- Origin and Evolution of Universe Solar System
- Geomorphology
- Climatology
- Oceanography
- Biogeography
- World Economic and Human Geography
- Important Places Mapping
Indian Geography
- Physical Geography of India
- Drainage System
- Indian Climate
- Soils
- Indian Flora & Faun
- Indian Economic and Human Geography
- Map Based Questions from India (Location of state, city, river, lakes, important places including Ramsar sites, Biosphere Reserves, Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Parks)
GENERAL STUDIES 2
Indian Polity
- Indian Constitution
- Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
- Separation of powers between various organs dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions.
- Comparison of the Indian Constitutional Scheme with that of Other Countries.
- Parliament and State Legislatures
- Structure, Organization and Functioning of the
- Salient Features of the Representation of People’s Act.
- Appointment to various Constitutional Posts, Powers, Functions and Responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies.
- Statutory, Regulatory and various Quasi-judicial Bodies.
Governance
Governance is commonly defined as the exercise of power or authority by political leaders for the well-being of their country’s citizens or subjects. It is the complex process whereby some sectors of the society wield power, and enact and promulgate public policies which directly affect human and institutional interactions, and economic and social development. A great deal about governance is the proper and effective utilization of resources.
Today, governance includes three sectors: the public sector (state actors and institutions), the private sector (households and companies), and the civil society (non-governmental organizations). These three sectors are said to work hand in hand in the process of governance.
- Governance- An introduction
- Governance: An Indian perspective
- Governance: Important aspects
- E-Governance
- Citizen Charters
- Appointment to various Constitutional posts, powers, functions and responsibilities of various constitutional bodies
- Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies
- Pressure Groups
- Role of Civil service in a democracy
- Elections in India
- Political parties in India
Social Justice
- Issues related to children
- Issues related to Minorities
- Issues related to Education Sector
- Issues related to SC/ST
- Issues related to Women
- Issues related to Elderly People
- Issues related to Health Sector
- Issues related to Third Gender & LGBTQIA
- Issues related to Rural Development
- Issues related to Urban Development
- Welfare Schemes
International Relations
- India and its neighborhood
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
- Important International Institutions, Agencies and Further Structure, Mandate etc.
GENERAL STUDIES 3
Economy
- Introduction to Economics
- National Income accounting
- Structure of Indian economy: a brief overview
- Planning in India
- Resource mobilization
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it
- Government budgeting
- Fiscal Policy
- The Reserve bank of India and monetary management
- Inflation
- Taxation system in India
- Indian financial system: Commercial Banking system
- Indian financial system-II: Money and capital market in India
- Investment models
- Infrastructure
- Agriculture
- Indian industries and economic growth
- Foreign trade and International organizations
- Poverty and unemployment
Agriculture
- Role of Agriculture in Indian Economy
- Major crops and cropping patterns in various parts of the country
- Irrigation and Irrigation Systems
- Agricultural Marketing and Issues
- e-Technology in the aid of farmers
- Farm Subsidies and MSP
- Public Distribution System
- Buffer Stocks and Food Security
- Economics of Animal-Rearing
- Food processing and related industries in India
- Land Reforms in India
Environment
- Basic Concepts Of Ecosystem
- Unique Ecosystems- Degradation And Management
- Biodiversity
- Environment Pollution And Control
- Climate Change And Associated Issues
- Environment Degradation And Issues
- Mining And Environment Issues
- Environment Impact Assessment
- Environmental Governance- National Legislation
- International Conventions
Disaster Management
- Background of Disaster management
- National Disaster Management Act, 2005
- National Policy on Disaster Management, 2009
- The National Disaster Management Plan, 2016
- Prime Minister’s Ten Point Agenda on DRR
- Agencies involved in Disaster Management
Science & Technology
- Biotechnology
- Space Technology
- Nuclear Technology
- Defence Technology
- Communication and IT Technology
- Nanotechnology
- Robotics
- Intellectual Property and Issues
- Contribution of Indians in Science & Technology
- Contribution of Science in Day to Day Life
Security Issues
- National Security
- Internal Security
- Extremism
- Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)
- Terrorism
- Money Laundering
- Cyber Security
- Role of Media and Social Networking Sites in Internal Security Challenges
GENERAL STUDIES 4
Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
- Ethics and Human Interface
- Human Values
- Attitude: Content, Structure, Function; its influence and relation with thought and behaviour; moral and political attitudes; Social influence and Persuasion
- Aptitude and foundational values for Civil Services
- Contributions of moral thinkers from India and the world
- Western philosophy and Indian philosophy related to Ethics
- Public or Civil Service Values
- Ethics in Public Administration
- Ethical issues in international relations and funding corporate governance
- Probity in Governance
- Emotional Intelligence – concepts and their utilities and application in administration and governance




