Definition, Components, Examples and Types of Ecosystem
Ecology can be defined as a scientific study of the interactions of organisms with their physical environment and
with each other.
The term ecology is derived from the Greek word ‘oikos’ meaning ‘house’, combined with the word ‘logy’ meaning the ‘science of’ or ‘the study of ’. Literally, ecology is the study of the earth as a ‘household’, of plants, human beings, animals and micro-organisms. They all live together as interdependent components.
A German zoologist Ernst Haeckel, who used the term as ‘oekologie’ in 1869, became the first person to use the term ‘ecology’. The study of interactions between life forms (biotic) and the physical environment (abiotic) is the science of ecology.
Contents
ECOSYSTEM
An ecosystem is a functional unit of nature, where living organisms interact among themselves and also with the
surrounding physical environment.
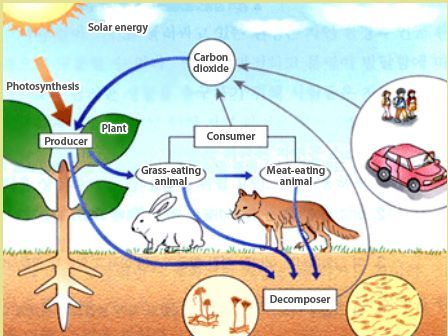
COMPONENTS OF ECOSYSTEM
There are four basic components of an ecosystem.
1. The abiotic part, which is the non-living environment.
2. The producers or autotrophs, the green plants capable of producing their own food by using the energy of sunlight to make carbohydrates from water and carbon dioxide; this process is called photosynthesis.
3. There are the consumers or heterotrophs. These are animals which obtain their food by eating plants or other animals. The heterotrophs in any ecosystem can be divided into groups by their feeding habits:
- herbivores eat only living plant material;
- Detritivores feed on dead plant and animal material;
- Carnivores eat other animals;
- Omnivores eat both plant and animal material.
4. Decomposers, such as the bacteria and fungi that promote decay
TYPES OF ECOSYSTEM
Ecosystem varies greatly in size from a small pond to a large forest or a sea. Many ecologists regard the entire biosphere as a global ecosystem, as a composite of all local ecosystems on Earth. Since this system is too much big and complex to be studied at one time, it is convenient to divide it into two basic categories, namely the terrestrial and the aquatic.
Terrestrial Ecosystem
- The ecosystem which is found only on landforms is known as the terrestrial ecosystem.
- The main factor which differentiates the terrestrial ecosystems from the aquatic ecosystems is the relative shortage of water in the terrestrial ecosystems and as a result the importance that water attains in these ecosystems due to its limited availability.
- Another factor is the better availability of light in these ecosystems as the environment is a lot cleaner in land than it is in water.
- The main types of terrestrial ecosystems are the forest ecosystems, the desert ecosystems, the grassland ecosystems and the mountain ecosystems.
Aquatic Ecosystem
- An ecosystem which exists in a body of water is known as an aquatic ecosystem.
- The aquatic ecosystems are mainly of two types, the freshwater ecosystems and the marine ecosystems.



